Microprocessors and -controllers
Microcontroller
MCU
An MCU is a group of microcontroller units that share a common architecture, design, and often the same core features
- ARM Cortex-M is a popular MCU family, where multiple manufacturers like STMicroelectronics, NXP, and Microchip produce MCUs that are based on the ARM Cortex-M core.
- AVR is another MCU family, famously used in the Arduino platform.
- PIC is a family of MCUs from Microchip Technology, with a range of devices from small 8-bit controllers to more powerful 16-bit and 32-bit versions.
Within each MCU family, you’ll typically see models that differ by features like:
- Flash memory size
- RAM size
- Clock speed
- Number of GPIO pins
- Peripheral support (e.g., UART, SPI, I2C, timers, etc.)
- the act of programming a microcontroller while it is already mounted on the board
- Contrary to Pre-Programming. You program the contro
CMSIS-DAP Devices are all devices that can write programs into a microcontroller's memory using JTAG or SWD. ler before soldering it somewhere.
Available Controllers
At least 5 of each:
- SEEEDSTUDIO XIAO SAMD21 NO HDRS
- SEEEDSTUDIO XIAO ESP32C3 NO HDRS
- SEEEDSTUDIO XIAO ESP32S3 NO HDRS
- SEEED STUDIO XIAO RP2040 ARDUINO
- ATSAMD11C14A-SSUT
- ATSAMD21E18A-AUT
- ATTINY412-SSFR
- ATTINY1624-SSFR
- ATTINY3226-SU
- AVR128DB32-I/PT
QFP mit Beinchen seitlich
TQFP ohne Beinchen
Soic-8 8 Beinchen
Punkt oder Kerbe kennzeichnen Pin 1
Putting code onto it
- the act of programming a microcontroller while it is already mounted on the board
- Contrary to Pre-Programming. You program the contro
CMSIS-DAP Devices are all devices that can write programs into a microcontroller's memory using JTAG or SWD. ler before soldering it somewhere.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- A standard synchronous serial communication interface used for short-distance communication between a main device and one or more peripheral devices.
- synchronous (needs clock signal), serial communication
- multiple secondary devices are possible
- full-duplex
- pins:
- MOSI (main out secondary in)
- MISO (main in secondary out)
- SCK (clock)
- SS (secondary select): select which secondary device to communicate with
Serial Peripheral Data Interface (SPDI)
- do not find any source for it
Joint Test Action Group (JTAG)
- eletronics manufacturers committee
- they developed a protocol with the same name
- mostly used for programming ARM cores
- pins
- TMS: mode select
- TCLK: clock
- TDO: data out
- TDI: data in
- nRESET: reset (optional)
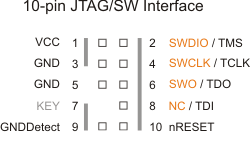
- two-pin variant of the JTAG protocol
- most common on newer ARM chips
- pins:
- swdio: in/out
- swclk: clock
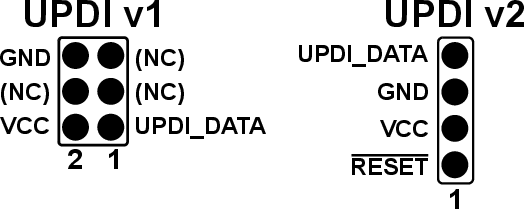
Unified Program and Debug Interface (UPDI)
- proprietary
- single-wire,
- bi-directional, half-duplex
- asynchronous
- can use off-the shelf UART adapters
- used to program AVR microcontrollers released since 2016, ATTINY412, ATTINY164.
- more detailed blog article
- debugging is hidden behind a proprietary interface, but even though you can snoop on the protocol with just a serial adapter and even though the large scale structure of the protocol is known too
- even more detailed article
- i did not find out what part of the protocol actually is proprietary and what not.
Difference between microcontroller and -processor
...