Microprocessors and -controllers
- audiobook of data sheet ATtiny212_412
- recitation
- literature explaining working with AVRs
- microcontroller vs -processor
MCU
An MCU is a group of microcontroller units that share a common architecture, design, and often the same core features
- ARM Cortex-M is a popular MCU family, where multiple manufacturers like STMicroelectronics, NXP, and Microchip produce MCUs that are based on the ARM Cortex-M core.
- AVR is another MCU family, famously used in the Arduino platform.
- PIC is a family of MCUs from Microchip Technology, with a range of devices from small 8-bit controllers to more powerful 16-bit and 32-bit versions.
Within each MCU family, you’ll typically see models that differ by features like:
- Flash memory size
- RAM size
- Clock speed
- Number of GPIO pins
- Peripheral support (e.g., UART, SPI, I2C, timers, etc.)
- the act of programming a microcontroller while it is already mounted on the board
- Contrary to Pre-Programming. You program the contro
CMSIS-DAP Devices are all devices that can write programs into a microcontroller's memory using JTAG or SWD. ler before soldering it somewhere.
Available Controllers
At least 5 of each:
- SEEEDSTUDIO XIAO SAMD21 NO HDRS
- SEEEDSTUDIO XIAO ESP32C3 NO HDRS
- SEEEDSTUDIO XIAO ESP32S3 NO HDRS
- SEEED STUDIO XIAO RP2040 ARDUINO
- ATSAMD11C14A-SSUT
- ATSAMD21E18A-AUT
- ATTINY412-SSFR
- ATTINY1624-SSFR
- ATTINY3226-SU
- AVR128DB32-I/PT
RP2040 (Raspberry Pi Pico)
Toolchain:
- Primary: Pico SDK (C/C++), CMake
- Alternatives: Arduino IDE (via Arduino-Pico Core), MicroPython/CircuitPython
Workflow:
- Write code in C/C++ or Python.
- Build with CMake (Pico SDK) or Arduino IDE.
- Flash via USB (UF2 bootloader) or SWD debugger (e.g., Picoprobe).
Efficiency Tips:
- Use Visual Studio Code with the Pico SDK extension for CMake integration.
- Leverage Picoprobe (a second Pico) for debugging.
ESP32 (Espressif)
Toolchain:
- Primary: ESP-IDF (C/C++), PlatformIO
- Alternatives: Arduino IDE (via ESP32 Core)
Workflow:
- Develop in C/C++ (ESP-IDF) or Arduino framework.
- Build with ESP-IDF CLI or PlatformIO.
- Flash via USB (esptool.py) or OTA updates.
Efficiency Tips:
- PlatformIO streamlines ESP-IDF/Arduino workflows.
- Use ESP-Prog or JTAG for advanced debugging.
SAMD21/SAMD11 (Atmel/Microchip)
Toolchain:
- Primary: Atmel/Microchip Studio (C/C++)
- Alternatives: Arduino IDE (via SAMD Core)
Workflow:
- Code in C/C++ (Microchip Studio) or Arduino.
- Build and flash via USB (UF2 bootloader) or EDBG/SWD.
Efficiency Tips:
- Use Arduino IDE for simplicity; enable verbose upload for debugging.
- For low-level control, use CMSIS libraries in Microchip Studio.
Attiny/AVR128 (AVR Family)
Toolchain:
- Primary: AVR-GCC + AVRdude
- Alternatives: Arduino IDE (via ATTiny Core)
Workflow:
- Write code in C/C++ or Arduino.
- Compile with AVR-GCC or Arduino IDE.
- Flash via ISP programmer (e.g., USBasp, Arduino-as-ISP).
Efficiency Tips:
- Use PlatformIO for project management.
- For tinyAVR (e.g., ATtiny85), optimize code size with
-Oscompiler flag.
General Workflow Optimization Tips
-
Unified Environments:
- PlatformIO (VS Code) supports all listed MCUs, reducing toolchain setup time.
- Arduino IDE (with board managers) simplifies entry-level development.
-
Debugging Tools:
- SWD/JTAG: Use for RP2040, ESP32, SAMD21 (e.g., Segger J-Link, CMSIS-DAP).
- Serial Monitor: Essential for ESP32/RP2040 debugging.
-
Version Control:
- Use
gitfor code management; track dependencies (e.g., submodules for Pico SDK).
- Use
-
Automation:
- Write Makefiles or use PlatformIO scripts for CI/CD pipelines.
QFP mit Beinchen seitlich
TQFP ohne Beinchen
Soic-8 8 Beinchen
Punkt oder Kerbe kennzeichnen Pin 1
Putting code onto it
- the act of programming a microcontroller while it is already mounted on the board
- Contrary to Pre-Programming. You program the contro
CMSIS-DAP Devices are all devices that can write programs into a microcontroller's memory using JTAG or SWD. ler before soldering it somewhere.
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- A standard synchronous serial communication interface used for short-distance communication between a main device and one or more peripheral devices.
- synchronous (needs clock signal), serial communication
- multiple secondary devices are possible
- full-duplex
- pins:
- MOSI (main out secondary in)
- MISO (main in secondary out)
- SCK (clock)
- SS (secondary select): select which secondary device to communicate with
Serial Peripheral Data Interface (SPDI)
- do not find any source for it
Joint Test Action Group (JTAG)
- eletronics manufacturers committee
- they developed a protocol with the same name
- mostly used for programming ARM cores
- pins
- TMS: mode select
- TCLK: clock
- TDO: data out
- TDI: data in
- nRESET: reset (optional)
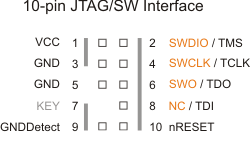
- two-pin variant of the JTAG protocol
- most common on newer ARM chips
- pins:
- swdio: in/out
- swclk: clock
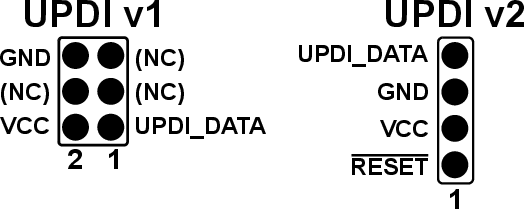
Unified Program and Debug Interface (UPDI)
- proprietary
- single-wire,
- bi-directional, half-duplex
- asynchronous
- can use off-the shelf UART adapters
- used to program AVR microcontrollers released since 2016, ATTINY412, ATTINY164.
- more detailed blog article
- debugging is hidden behind a proprietary interface, but even though you can snoop on the protocol with just a serial adapter and even though the large scale structure of the protocol is known too
- even more detailed article
- i did not find out what part of the protocol actually is proprietary and what not.
Difference between microcontroller and -processor
...